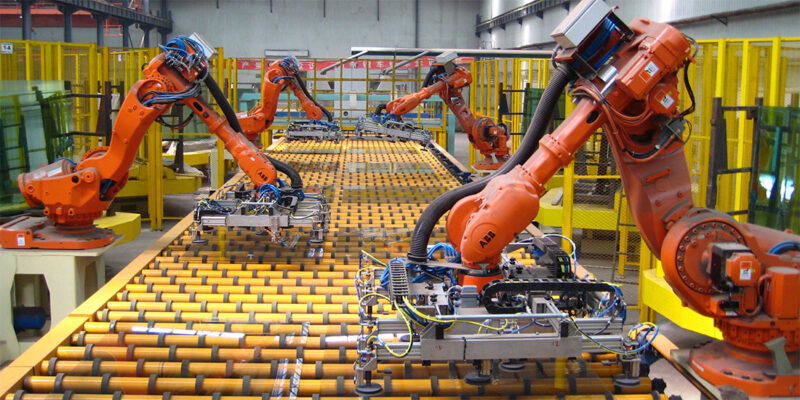
The manufacturing industry in the United States has a long and storied history, evolving from the early days of industrialization to the modern era of automation. However, the landscape of manufacturing is changing rapidly. Faced with challenges like labor shortages, rising operational costs, and increasing global competition, US manufacturers are turning to advanced technologies to stay competitive. Among these technologies, assembly robots are playing a crucial role in transforming production lines across the country.
How Assembly Robots are Revolutionizing Production Lines
Assembly robots have a profound impact on boosting efficiency and productivity in production lines. Unlike humans, robots can operate continuously without fatigue, which significantly shortens cycle times and increases overall output. Their ability to perform tasks with consistent precision helps minimize errors commonly associated with manual processes. For instance, in the electronics industry, robots can accurately place small components on circuit boards, ensuring high-quality assembly at a faster rate.
Though the upfront cost of robotics may be substantial, the long-term financial benefits often outweigh the initial investment. By improving efficiency, reducing waste, and minimizing downtime, robots can significantly lower operational costs. Over time, the return on investment (ROI) for businesses that integrate robotics into their operations can be substantial. For small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), various financing options and leasing programs can make robotic solutions more affordable, enabling them to remain competitive in an increasingly automated market.
Technological Advancements Driving the Adoption of Assembly Robots
The combination of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning with robotics is transforming the industry. With AI, robots gain the ability to learn from past experiences, adjust to new tasks, and even anticipate and address potential problems. For example, AI-powered robots can identify trends in production data and fine-tune their operations based on these insights, resulting in enhanced efficiency and higher-quality outcomes.
Advancements in Robotics Hardware
Robotics hardware has also seen significant advancements, particularly in robot manufacturing processes. Modern robots are equipped with advanced sensors that allow them to ‘see’ and ‘feel’ their environment, making them more adaptable to different tasks. Grippers and end-effectors have become more sophisticated, enabling robots to handle delicate objects with precision. Additionally, the rise of 5G and the Internet of Things (IoT) is enhancing connectivity between robots and other manufacturing systems, allowing for seamless communication and real-time data exchange.
Some tools even come with basic setup and intuitive programming, so that no experience in engineering is needed. For example, the Vectis automation tool for welding provides robotic welding with a modular fixturing cart, so that it can be run on site with no anchoring or dedicated footprint required.
User-Friendly Interfaces and Programming
Gone are the days when programming robots required extensive coding knowledge. Today, user-friendly interfaces and low-code/no-code platforms are making it easier for manufacturers to deploy and operate robots. These platforms allow operators to program robots using drag-and-drop interfaces or simple visual tools, reducing the learning curve and enabling faster deployment.
Impact on the US Manufacturing Sector
Assembly robots are essential in helping US manufacturers stay competitive in the global market. By automating repetitive and precise tasks, robots lower production costs and enhance product quality. This improved efficiency allows US companies to better compete with international rivals, especially those from regions with lower labor costs. Moreover, the efficiency gains from robotics are supporting the trend of reshoring production, which brings manufacturing jobs back to the US.
Job Market Transformation
The rise of robotics in manufacturing has raised concerns about job losses, but the reality is more complex. Instead of displacing workers, robots are shifting human roles towards higher-value activities. As robots handle routine and repetitive tasks, employees can concentrate on more intricate and innovative aspects of production. This shift also creates new career paths in areas such as robotics programming, maintenance, and systems integration, where there is growing demand for skilled professionals.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Sustainability is becoming increasingly important in manufacturing, and assembly robots are aiding in the adoption of greener practices. By operating with high precision, robots help reduce waste and minimize the consumption of raw materials. They also enhance energy efficiency by optimizing production processes and decreasing the need for rework. Consequently, companies that integrate robotics can lower their environmental impact while achieving better financial performance.
Challenges and Considerations in Adopting Assembly Robots
The expense of acquiring and setting up robotics can pose a significant challenge for many manufacturers, especially small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). While larger companies might have the resources to invest in cutting-edge robotic systems, smaller businesses often face difficulties with the initial financial outlay. Despite this, the long-term advantages—such as improved efficiency and lower operational costs—often make the investment worthwhile. For SMEs, options like leasing or robotics-as-a-service (RaaS) can provide more accessible pathways to adopting robotic technology.
Technical Integration and Maintenance
Incorporating robots into existing production lines can be technically demanding, especially in facilities with outdated equipment or processes. Effective implementation involves careful planning, including evaluating compatibility and potentially upgrading current systems. Moreover, maintaining and troubleshooting robotic systems requires specialized expertise, which may involve training current employees or hiring new personnel with the necessary skills.
Cybersecurity Concerns
With the increased connectivity brought about by robotics, AI, and the Internet of Things (IoT), cybersecurity risks also rise. Connected robots are susceptible to cyberattacks that could disrupt operations or expose sensitive information. It is essential for manufacturers to prioritize cybersecurity by employing robust protective measures such as encryption, firewalls, and regular security audits to safeguard their operations from potential threats.
Conclusion
Assembly robots are revolutionizing production lines across the United States, offering a path forward for an industry facing significant challenges. By enhancing efficiency, addressing labor shortages, and enabling new levels of precision and sustainability, these robots are reshaping the future of manufacturing. As technology continues to advance, the role of robotics in production will only grow, driving the US manufacturing sector toward greater global competitiveness and innovation. Embracing this future will require manufacturers to balance technology with human ingenuity, creating a workforce and production environment that leverages the best of both worlds.