Introduction
In today’s data-driven world, managing and organizing data efficiently is crucial for individuals and businesses alike. The concept of data hierarchy plays a significant role in ensuring data is structured, organized, and easily accessible. Data hierarchy is the systematic arrangement of data into different levels based on its meaning and significance. This article explores the various levels of data hierarchy, their importance, and their applications across different sectors.
What is Data Hierarchy?
-
Definition
Data hierarchy refers to the categorization of data into distinct levels based on their relevance and usefulness. Each level represents a different degree of data organization and complexity, contributing to better decision-making and analysis.
-
Importance of Data Hierarchy
Data hierarchy is essential because it provides structure to raw data, making it more manageable and interpretable. It enables businesses and individuals to extract valuable insights from data, leading to informed actions and better outcomes.
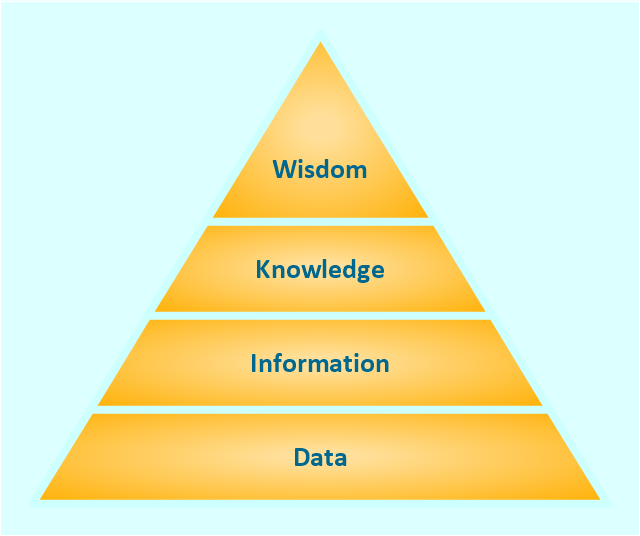
Levels of Data Hierarchy
Data hierarchy consists of four primary levels, each building upon the previous one to create a comprehensive data structure.
-
Level 1: Raw Data
At the base level of data hierarchy, we have raw data. This unorganized and unprocessed data is the foundation of all information. Raw data lacks context and meaning, and it requires further processing before it becomes valuable.
- Characteristics of Raw Data
- Unstructured and unordered
- Contains individual data points
- Requires cleansing and formatting
- Examples of Raw Data
- Temperature readings from various sensors
- Customer names and contact information
-
Level 2: Information
The next level in data hierarchy is information. At this stage, raw data undergoes processing and analysis, becoming more meaningful and usable. Information provides context to the data, making it comprehensible to users.
- Characteristics of Information
- Processed and organized
- Provides answers to specific questions
- Contextual and relevant
- Examples of Information
- Monthly sales reports
- Weather forecasts
-
Level 3: Knowledge
Above information, we find knowledge. Knowledge is a deeper understanding derived from analyzing various pieces of information. It involves interpreting patterns, trends, and relationships within the data.
- Characteristics of Knowledge
- Derived from analyzing information
- Enables making informed decisions
- Provides insights and understanding
- Examples of Knowledge
- Market trends analysis
- Customer behavior patterns
-
Level 4: Wisdom
The highest level of data hierarchy is wisdom. Wisdom is the result of critically evaluating knowledge and using it to make strategic decisions. Wisdom involves applying experience, intuition, and ethical considerations.
- Characteristics of Wisdom
- Integrates knowledge with experience
- Involves complex decision-making
- Addresses long-term implications
- Examples of Wisdom
- Business strategy formulation
- Ethical decision-making in healthcare
- Understanding Each Level in Detail
Data Hierarchy in Business and Technology
The concept of data hierarchy finds extensive applications in various industries, especially in business and technology.
-
Data Management and Analysis
In business, effective data management and analysis are crucial for success. Data hierarchy ensures that data is stored, organized, and accessed efficiently, making it easier for organizations to extract valuable insights.
-
Data-driven Decision Making
Data-driven decision making relies on data hierarchy to convert raw data into meaningful information and knowledge. This approach enables businesses to make informed choices based on accurate data analysis.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Data Hierarchy
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning play a significant role in data hierarchy. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data quickly, extracting valuable patterns and knowledge.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Data Hierarchy
Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of data hierarchy can help businesses implement it effectively.
-
Advantages
- Improved data organization: Data hierarchy provides a structured framework for organizing data, making it easier to manage.
- Enhanced data analysis: Categorizing data into levels allows for more targeted analysis and better decision-making.
-
Disadvantages
- Complex implementation: Implementing data hierarchy may require significant effort, especially for large datasets.
- Limited flexibility: Data hierarchy may not accommodate unforeseen data variations, leading to potential data management challenges.
Best Practices for Implementing Data Hierarchy
To leverage data hierarchy effectively, organizations should follow some best practices.
- Data Organization
Ensure that data is appropriately categorized into the relevant hierarchy levels, facilitating easy access and analysis.
- Data Security
Implement robust security measures to protect data at all hierarchy levels, safeguarding it from unauthorized access and breaches.
Future Trends in Data Hierarchy
As technology continues to evolve, data hierarchy will also undergo changes. New advancements may lead to more efficient and automated data categorization processes.
Conclusion
Data hierarchy is a fundamental concept that empowers businesses and individuals to make sense of vast amounts of data. From raw data to wisdom, each level of data hierarchy contributes to informed decision-making and strategic planning. Implementing data hierarchy effectively can unlock valuable insights, paving the way for growth and success in a data-driven world.
FAQs
- What is the main purpose of data hierarchy?
The main purpose of data hierarchy is to categorize data into different levels, making it more organized and accessible for analysis and decision-making.
- How is data hierarchy used in machine learning?
In machine learning, data hierarchy helps in organizing and preprocessing data, making it suitable for training algorithms and improving model performance.
- Is data hierarchy relevant in small businesses?
Yes, data hierarchy is relevant for businesses of all sizes. It helps small businesses organize and utilize their data effectively.
- Can data hierarchy help prevent data breaches?
Implementing data hierarchy with robust security measures can contribute to preventing data breaches by limiting unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- What are the challenges in implementing data hierarchy?
Some challenges in implementing data hierarchy include handling large and diverse datasets, ensuring data accuracy, and adapting to evolving technological changes.